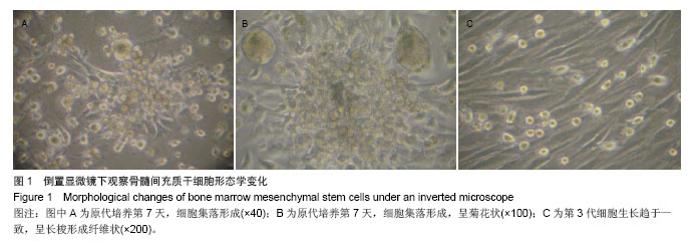
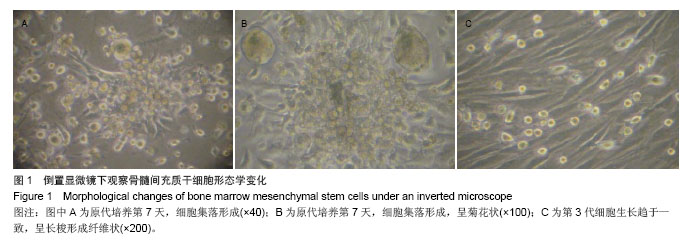
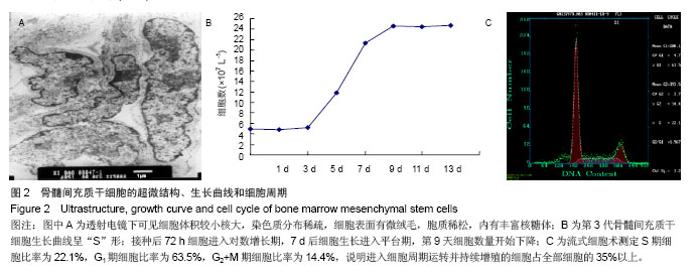
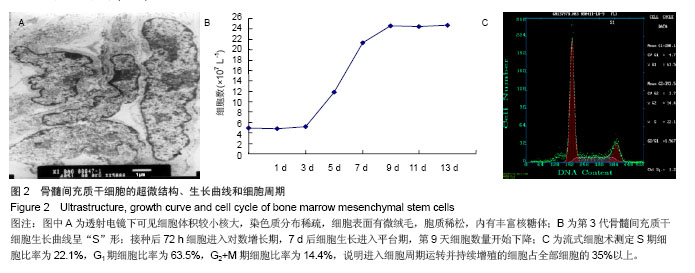
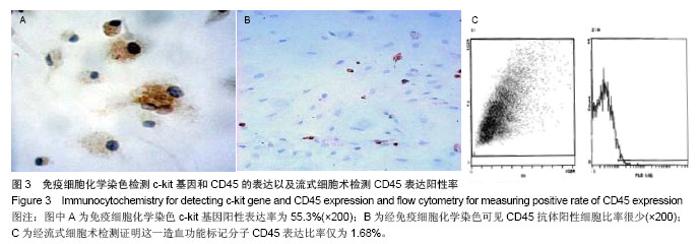
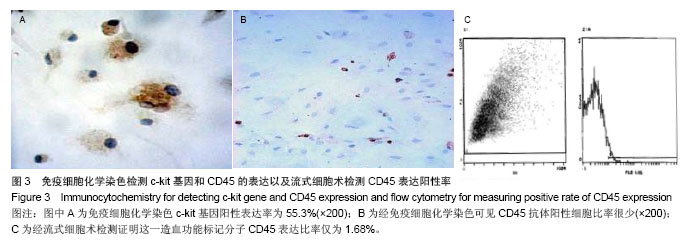
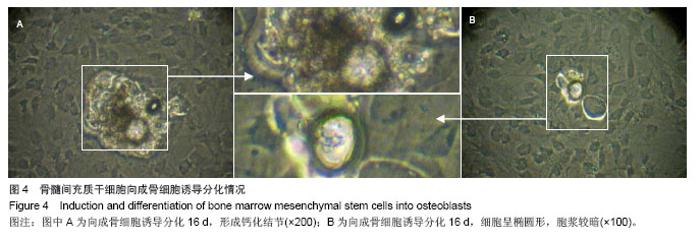
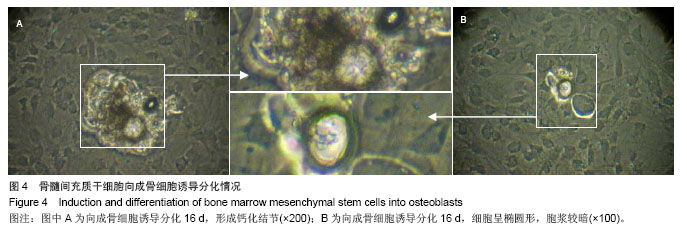
| [1]Busb WD,Jamali A,Chu C,et al. Fresh osteochondral allografting ofthe patellofemoral joint. AmericanAcademy of OrthopaedicSurgeons 68th Annual Meeting(AAOS). 2001: 177.
[2]Grande DA, Breitbart AS, Mason J,et al. Cartilage tissue engineering: current limitations and solutions.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(367 Suppl):S176-185.
[3]Aubin PP, Cheah HK, Davis AM,et al. Long-term followup of fresh femoral osteochondral allografts for posttraumatic knee defects.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(391 Suppl):S318-327.
[4]Matsumoto T, Okabe T, Ikawa T, et al. Articular cartilage repair with autologous bone marrow mesenchymal cells.J Cell Physiol. 2010;225(2):291-295.
[5]Khan WS, Johnson DS, Hardingham TE.The potential of stem cells in the treatment of knee cartilage defects.Knee. 2010; 17(6):369-374.
[6]Bruder SP, Jaiswal N, Ricalton NS,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells in osteobiology and applied bone regeneration.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(355 Suppl):S247-256.
[7]Nuttall ME, Patton AJ, Olivera DL,et al. Human trabecular bone cells are able to express both osteoblastic and adipocytic phenotype: implications for osteopenic disorders.J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(3):371-382.
[8]Zohar R, Sodek J, McCulloch CA.Characterization of stromal progenitor cells enriched by flow cytometry.Blood. 1997;90(9): 3471-3481.
[9]Fortier LA, Nixon AJ, Williams J,et al. Isolation and chondrocytic differentiation of equine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Am J Vet Res. 1998;59(9): 1182-1187.
[10]Ghilzon R, McCulloch CA, Zohar R.Stromal mesenchymal progenitor cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 1999;32(3-4):211-221.
[11]Lin SC, Liu CL, Wang TI,et al. Clinical implications of C-kit gene mutation in patients with large gastrointestinal stromal tumors.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21(10):1604-1608.
[12]Turin L, Acocella F, Stefanello D,et al.Expression of c-kit proto-oncogene in canine mastocytoma: a kinetic study using real-time polymerase chain reaction.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2006; 18(4):343-349.
[13]Kimura K, Song CH, Rastogi A,et al.Interleukin-3 and c-Kit/stem cell factor are required for normal eosinophil responses in mice infected with Strongyloides venezuelensis. Lab Invest. 2006;86(10):987-996. |